How It Works
Pillar connects a co-pilot chat interface to your application's functionality through Actions and Plans.
The Flow
When a user asks a question, Pillar:
"How do I invite a team member?"
Finds relevant docs and matches actions by semantic similarity.
Returns helpful steps plus suggests the "Invite Member" action.
Your handler executes and opens the invite modal.
Actions
Actions are the core integration point between Pillar's co-pilot and your application. They represent things users can do—like navigating to a page, opening a modal, or triggering a workflow.
You define actions in your code with descriptions the co-pilot can understand:
// lib/pillar/actions/index.tsimport type { SyncActionDefinitions } from '@pillar-ai/sdk';export const actions = {invite_member: {description: 'Open the invite team member modal',examples: ['invite someone', 'add a user', 'how do I add teammates?'],type: 'trigger_action' as const,},view_settings: {description: 'Navigate to the settings page',type: 'navigate' as const,path: '/settings',autoRun: true,},} as const satisfies SyncActionDefinitions;export default actions;
When the co-pilot suggests an action, users can click to execute it—or for simple navigations, it can run automatically.
Action Types
Pillar supports different action types for different use cases:
| Type | What It Does | Example |
|---|---|---|
navigate | Goes to a page in your app | Settings, dashboard, detail pages |
trigger_action | Runs your custom logic | Opens modals, starts wizards, toggles features |
inline_ui | Shows interactive UI in the chat | Confirmation forms, data previews |
external_link | Opens a URL in a new tab | Documentation, external resources |
copy_text | Copies text to clipboard | API keys, code snippets |
Handlers
Each action has a handler—your code that runs when the action is triggered:
invite_member: {description: 'Invite a team member',type: 'trigger_action',handler: (data) => {// This runs when the user triggers the actionopenInviteModal({ email: data.email });},}
Handlers can do anything: call your APIs, update state, navigate, open modals. The co-pilot extracts relevant data from the conversation and passes it to your handler.
Plans
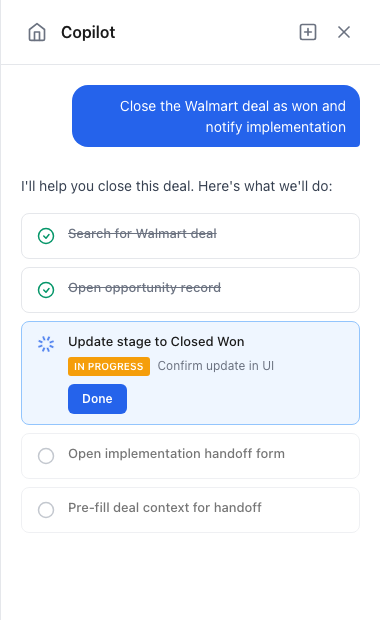
When users ask for help with complex tasks, Pillar's co-pilot automatically chains your actions together into a Plan—a guided checklist that walks them through the process.
You don't define these workflows. You define small, focused actions. The co-pilot figures out how to combine them.
"Help me set up my workspace"
The co-pilot looks at your available actions and creates a checklist: Create a project → Add a knowledge source → Configure the assistant → Invite your team.
Each step is presented one at a time with clear instructions.
Your registered handlers execute as the user progresses through the plan.
This is a key power of Pillar: define simple actions once, and the co-pilot composes them into complex workflows on the fly. No need to anticipate every multi-step task your users might need—just build the building blocks.
Context
Context tells Pillar what the user is currently doing, enabling:
- Smarter responses based on the current page or feature
- Action filtering based on user role or permissions
- Error-aware help when the user is facing an issue
pillar.setContext({currentPage: '/settings/billing',currentFeature: 'Billing Settings',userRole: 'admin',errorState: { code: 'PAYMENT_FAILED', message: 'Card declined' },});
With this context, the co-pilot knows the user is on the billing page and can provide relevant help.
Architecture Overview
The Pillar SDK lives entirely in your frontend. It connects to Pillar's backend for AI capabilities, while your action handlers connect to your own backend.
What Lives Where
Your Frontend
PillarProvider— Initializes the SDK with your project credentialsdefineActions— Registers actions with descriptions the co-pilot understandssetContext— Sends current page/user state for smarter responsesPillarPanel— The chat UI component users interact with
Pillar Backend
- Knowledge Base — Your indexed documentation and help content
- Action Registry — Synced definitions of available actions
- AI / RAG — Processes queries, retrieves relevant content, generates responses
Your Backend
- Your APIs and data, called by your action handlers when users trigger actions
Data Flow
-
SDK → Pillar: The SDK syncs your action definitions and context to Pillar's backend. When users ask questions, the panel sends queries to Pillar for co-pilot responses.
-
Actions → Your Backend: When a user triggers an action, the handler you defined runs in your frontend. That handler can call your own APIs, navigate pages, open modals—whatever you wrote it to do.
The SDK never talks to your backend directly. Your action handlers do. This keeps authentication and data access fully under your control.
Key Concepts
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Actions | Things users can do in your app, defined with descriptions the co-pilot understands |
| Plans | Multi-step workflows the co-pilot creates from your actions |
| Context | Information about what the user is doing for smarter co-pilot responses |
What Happens When
| User Action | What Pillar Does |
|---|---|
| Opens panel | Loads chat UI, shows greeting or recent conversation |
| Asks a question | Searches knowledge base, matches to actions, responds |
| Clicks suggested action | Calls your registered handler with extracted data |
| Starts a plan | Creates checklist, executes steps as user progresses |
| Selects text + asks | Opens panel with selection as context |
When Pillar Doesn't Know
Sometimes users ask questions that Pillar can't fully answer—maybe there's no relevant documentation, or the request doesn't match any defined action. Here's how Pillar handles these cases and how you can improve over time.
How the Agent Responds
When Pillar encounters a query it can't confidently handle, it will:
- Acknowledge the limitation — Rather than making something up, Pillar tells the user it's unsure or doesn't have information on that topic
- Offer alternatives — It may suggest related actions or point to general resources that might help
- Invite escalation — Depending on your configuration, it can offer to escalate to human support. You can add a "Talk to Human" tab in the sidebar that triggers your existing support tools (Intercom, Zendesk, etc.) with the conversation history pre-filled. See the Human Escalation guide for implementation details.
"How do I integrate with Stripe?"
No knowledge base content matches. No actions are relevant.
"I don't have specific documentation about Stripe integration. Would you like me to connect you with our support team?"
Reviewing Failed Queries
The Pillar dashboard provides tools to identify and fix these gaps:
-
Conversations page — Review all user conversations with filtering by:
- Negative feedback (thumbs down)
- Abandoned conversations
- Escalated requests
-
Query clustering — Pillar automatically groups similar queries, helping you spot patterns like "lots of users asking about X but we have no docs for it"
-
Reasoning traces — See exactly how Pillar processed each query: what it searched for, what sources it found (or didn't find), and why it responded the way it did
Creating Corrections
When you find a response that missed the mark, you can create a correction directly from the conversation view:
- Open the conversation detail drawer
- Select the relevant quotes from the conversation or reasoning trace
- Write a correction explaining what the right answer should be
Pillar processes your correction and uses it to improve future responses to similar queries.
| Gap Type | How to Fix It |
|---|---|
| Missing knowledge | Add content to your knowledge base |
| Wrong action suggested | Improve action descriptions or add examples |
| Incorrect response | Create a correction from the conversation |
| No action exists | Define a new action in your code |
Next Steps
- React Quickstart — Get started with React
- Setting Up Actions — Define actions for your app
- Plans — Learn about multi-step workflows
- Adding Context — Provide user context for smarter responses